APT Packages
apt-cache search and apt show
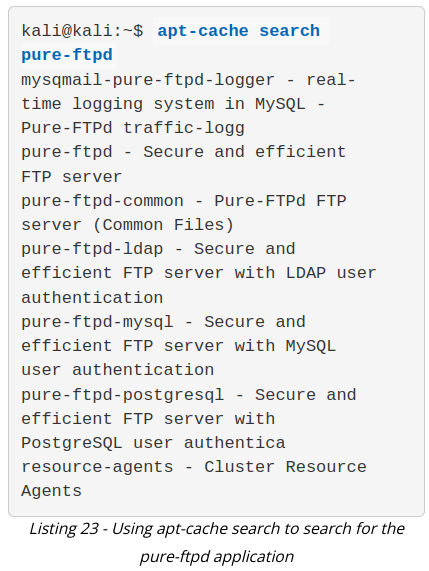
The apt-cache search command displays much of the information stored in the internal cached package database. For example, let's say we would like to install the pure-ftpd application via APT. The first thing we have to do is to find out whether or not the application is present in the Kali Linux repositories. To do so, we would proceed by passing the search term on the command line:
To confirm that the resource-agents package description really contains the "pure-ftpd" keyword, pass the package name to apt show as follows:
apt remove --purge
The apt remove --purge command completely removes packages from Kali. It is important to note that removing a package with apt remove removes all package data, but leaves usually small (modified) user configuration files behind, in case the removal was accidental. Adding the --purge option removes all the leftovers.
dpkg
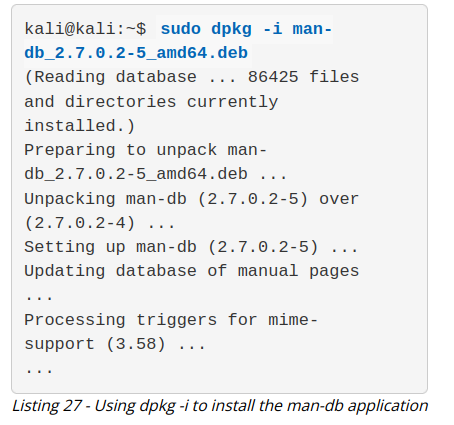
dpkg is the core tool used to install a package, either directly or indirectly through APT. It is also the preferred tool to use when operating offline, since it does not require an Internet connection. Note that dpkg will not install any dependencies that the package might require. To install a package with dpkg, provide the -i or --install option and the path to the .deb package file. This assumes that the .deb file of the package to install has been previously downloaded or obtained in some other way.

No Comments